168幸运飞开艇查询开奖结果,新168飞艇历史记录查询号码 EFEKTOWNA AERODYNAMICZNA ŁATWA W OBSŁUDZE LEKKA
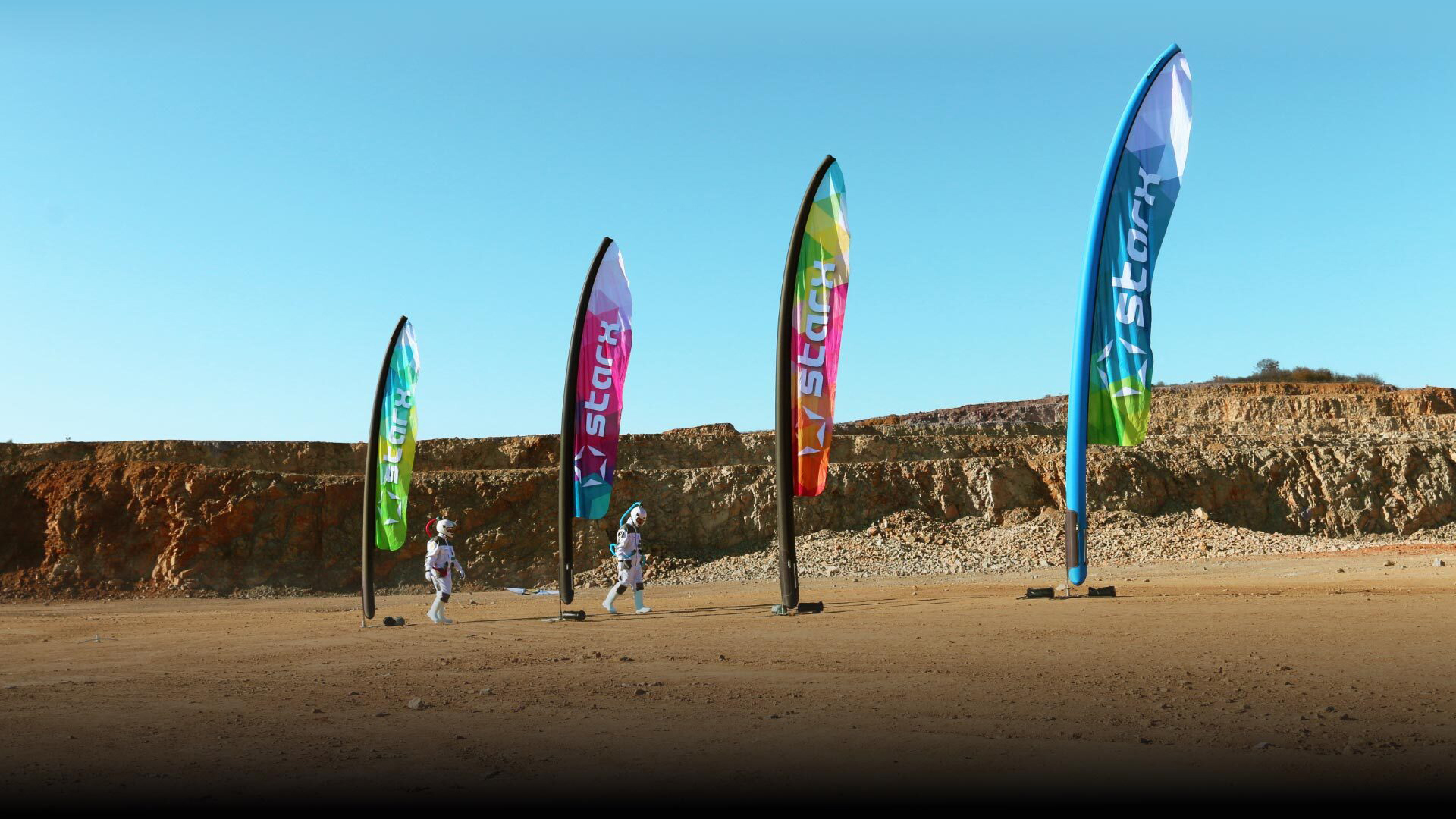
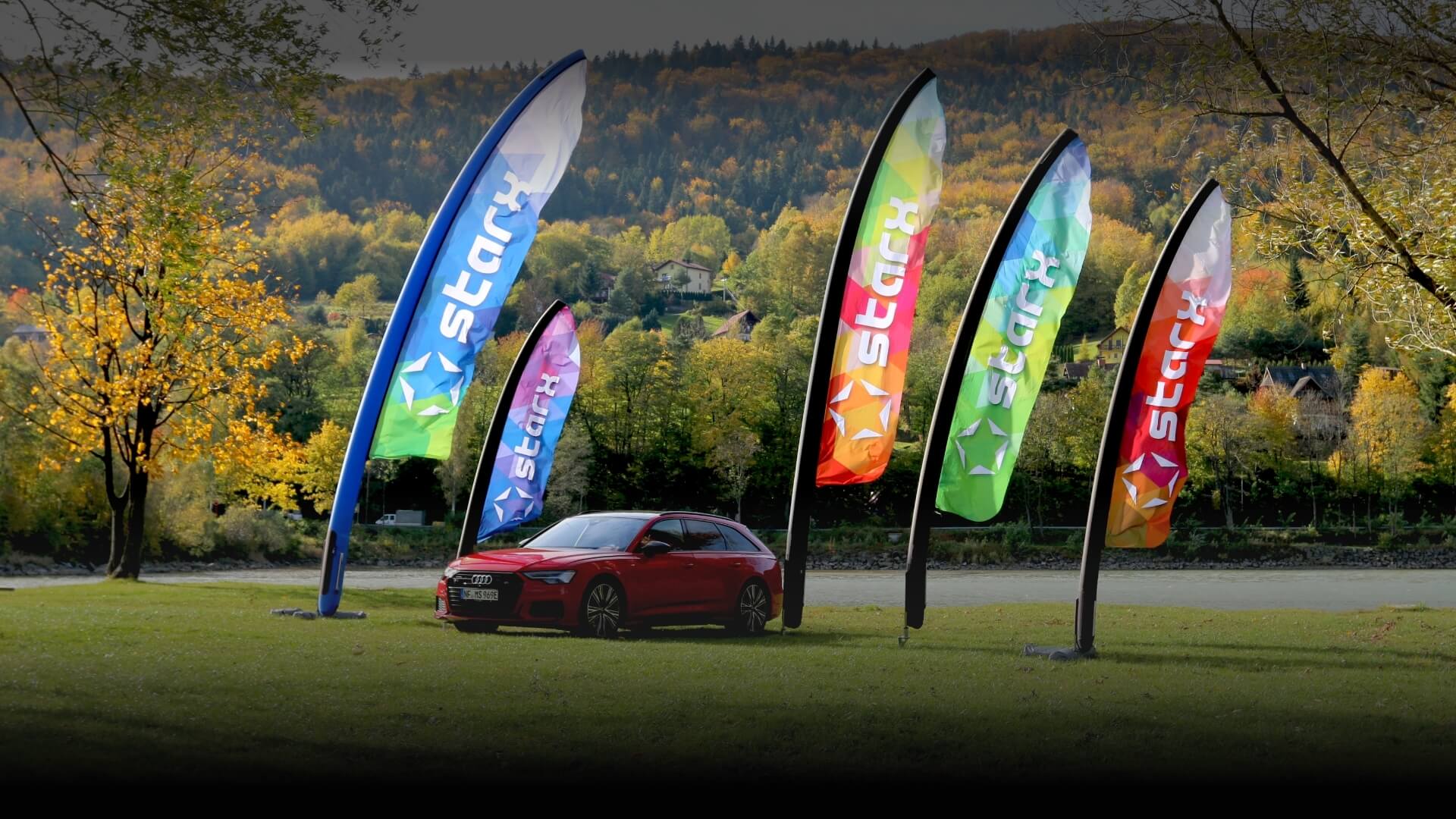
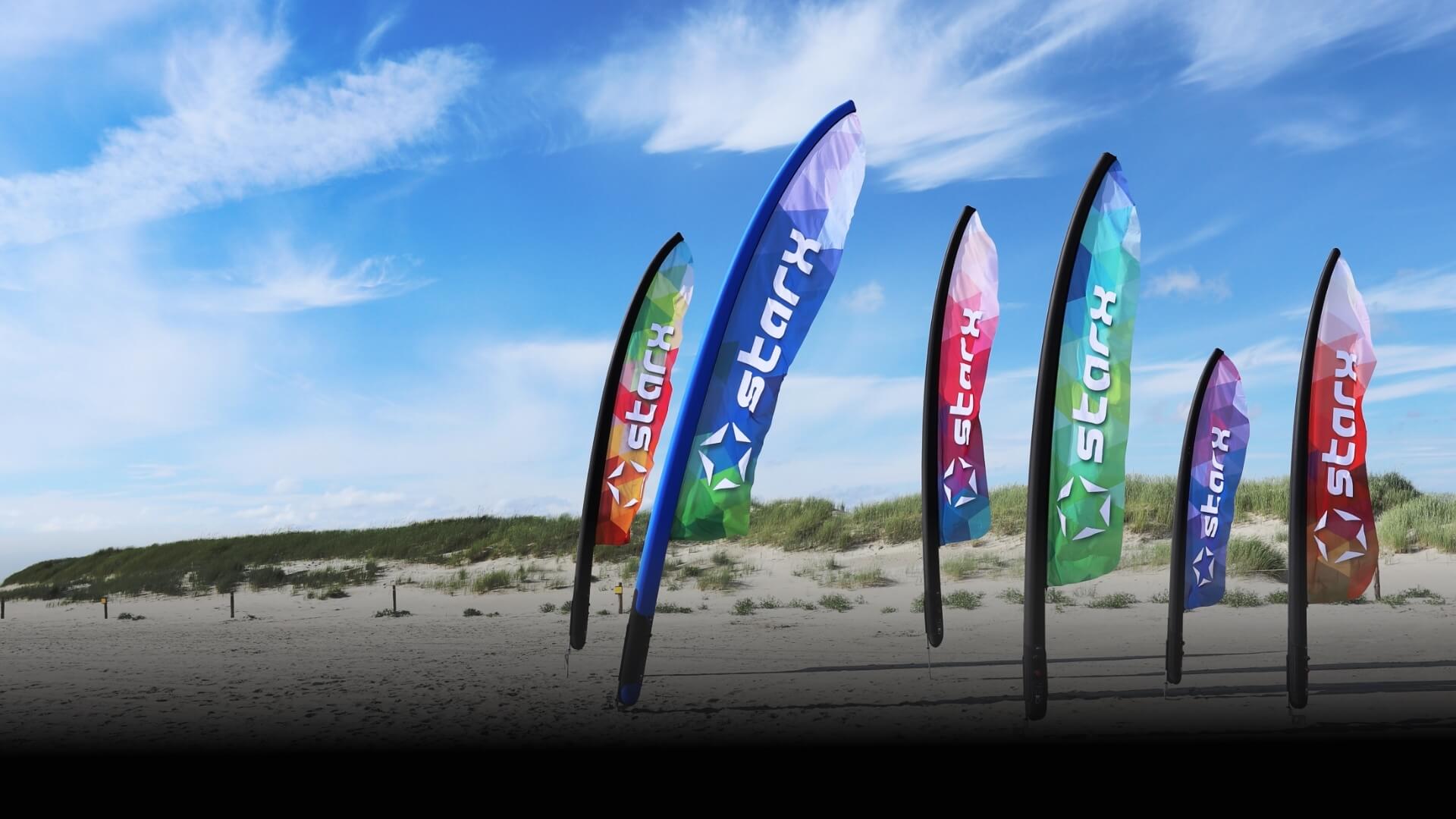
幸运飞行艇官方开奖号码查询,历史记录查询. Jeszcze nigdy żaden nośnik promocyjny nie łączył tych wszystkich cech w tak bezkompromisowy sposób. Wspaniały DESIGN, wysoka JAKOŚĆ I ESTETYKA wykończeń sprawiają że produkt doskonale nadaje się do promocji każdej marki, bez względu na to, czy odbywa się ona na plaży, ekskluzywnym wnętrzu, koncercie, czy wydarzeniu sportowym.
Oryginalna Flaga Pneumatyczna STARX – wyjątkowe wsparcie dla brandu w każdych warunkach, dzięki zastosowaniu szerokiej gamy podstaw STARX.
PATENT
ORGINALNY PRODUKT STARX
Nasi projektanci sprostali wyzwaniu, stworzyli niesamowity produkt, którego wcześniej nie było. Nie ma żadnej oryginalnej flagi pneumatycznej poza STARX.
Produkty Starx stanowią chronione oraz zgłoszone do ochrony do urzędu patentowego RP oraz Urzędu Unii Europejskiej ds. własności intelektualnej przedmioty własności przemysłowej w postaci wynalazków, wzorów użytkowych i wzorów przesyłowych. Korzystając z oryginalnych rozwiązań pneumatycznych Strax nie naruszasz praw własności intelektualnej. W przypadku dalszych pytań napisz do: info@starxflag.com
Czytaj więcej

168体彩飞艇开奖精准直播,官方飞行艇记录查询网站 TECHNOLOGIA WYPEŁNIANA POWIETRZEM
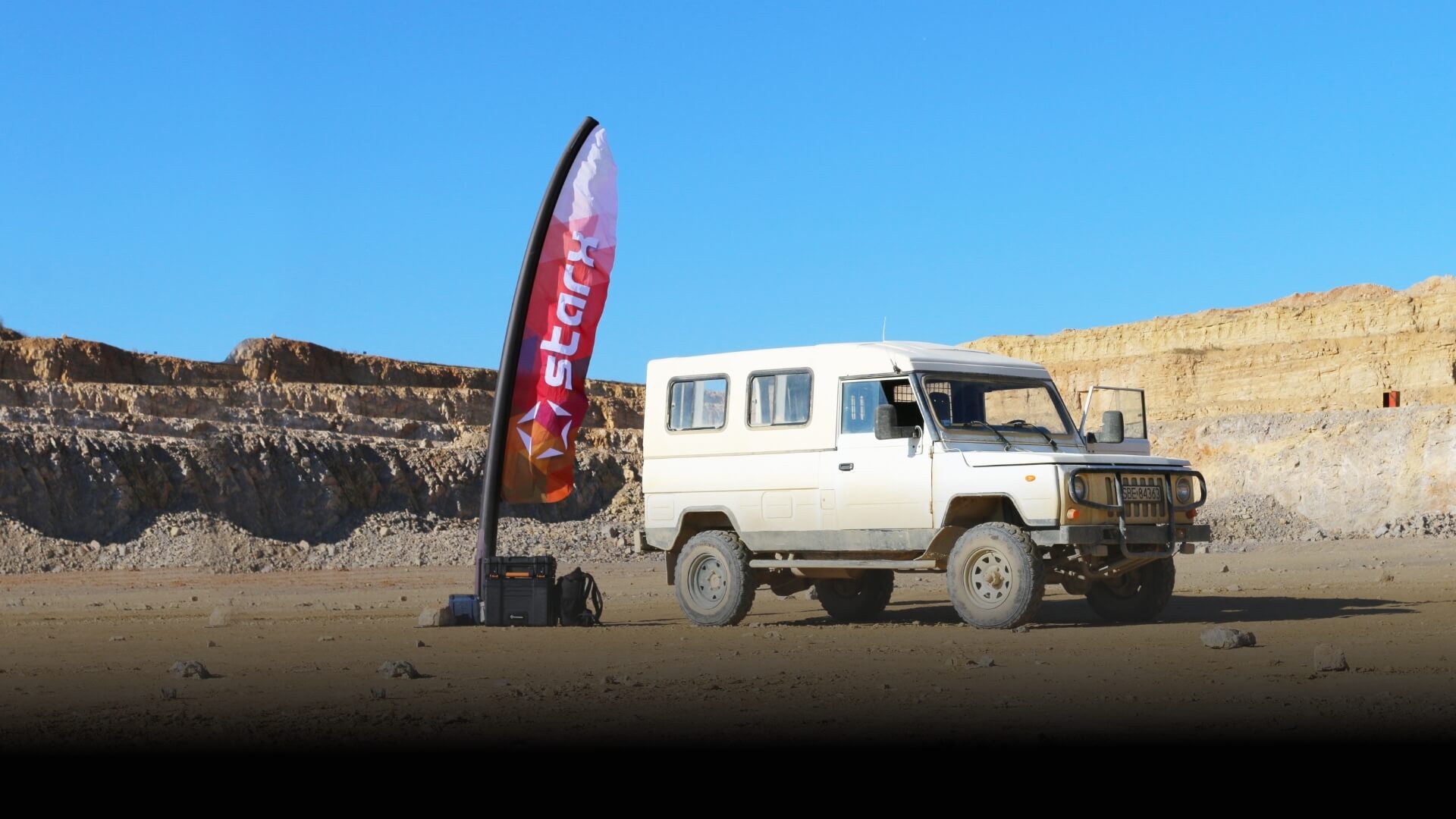
实时数据168体彩飞艇开奖网·飞艇官方168全天计划精准直播. Flagi Starx zostały zaprojektowane i wykonane przy wykorzystaniu najnowocześniejszych dostępnych materiałów i technologii. Tradycyjne, szczególnie te większe maszty flagowe, kojarzą się zazwyczaj z ciężkimi, metalowymi elementami, do których złożenia często wymagane jest użycie specjalistycznych narzędzi.
Flagi Starx to zupełnie nowa era nośników reklamowych, które dzięki sprężonemu powietrzu dają się rozstawić w niezwykle krótkim czasie, osiągając nieporównywalnie większe rozmiary. Wszystko to dzięki połączeniu wewnętrznego wkładu szczelnego wykonanego z TPU z zewnętrznym poszyciem wykonanym technologią w jakiej wykonuje się profesjonalny sprzęt sportowy.
Maszt pompuje się za pomocą pompki ręcznej lub elektrycznej przez wentyl, a nad regulacją ciśnieni czuwa system regulacji ciśnienia OVER PRESSURE. Flaga Starx została stworzona dla promocji brandu tak żeby było łatwiej, bezpieczniej, lżej i efektowniej.
Czytaj więcej
ZOSTAŃ DYSTRYBUTOREM
Ten produkt jest innowacyjny, profesjonalny i robi wrażenie na każdym kto miał z nim styczność. Wspaniałe produkty wymagają wspaniałych sprzedawców, wspaniali sprzedawcy wymagają wspaniałych wyzwań. Nie zwlekaj i dołącz do grona dystrybutorów sprzedających flagi STARX. Sprawdź, czy w twoim regionie nadal istnieje taka możliwość kontaktując się z nami pod: distributor@starxflag.com